Passive components are the unsung heroes of modern electronics. And despite not generating power, they play a key role in the functionality and reliability of electronic circuits. From simple gadgets to complex machinery, these components ensure that everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
And if you’re involved with modern electronics, their design, and maintenance, you need to learn what role these tiny things play and how they are applied in our everyday electronics.
This article will explore various passive components used in electronic circuits, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Also, learn about the Geekzilla Podcast by reading this article!
We’ll delve into their functions, applications, and significance in modern electronics. Other than that, we’ll highlight the importance of chokes and inductors in ensuring circuit efficiency and stability.
Understanding Resistors
Resistors are one of the most basic passive components you can find in any electronic circuit.
They basically work by limiting the flow of electric current, making sure that other components receive the appropriate voltage.
Resistors come in various types, such as fixed, variable, and special resistors like thermistors and photoresistors, to name a few. Each type has unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications.
Fixed resistors are commonly used to set the biasing conditions of transistors and other components. Variable resistors, like potentiometers, allow for adjustable resistance, which is useful in applications requiring fine-tuning.
Thermistors change resistance with temperature variations, making them ideal for temperature sensing and control. Photoresistors can control how strong the light is and alter the resistance based on that light, it is usually used in light-sensitive devices.
The Role of Capacitors
Capacitors are another must-have passive component known for their ability to store and release electrical energy.
They are used in a variety of applications, such as filtering, timing, and coupling signals between different stages of a circuit. Capacitors come in different types, including ceramic, electrolytic, and tantalum, each with specific characteristics suited to particular applications.
Ceramic capacitors are widely used for their stability and low cost, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. Electrolytic capacitors offer higher capacitance values, making them suitable for power supply filtering and energy storage.
Tantalum capacitors provide excellent reliability and long life, often used in industrial applications where performance is paramount.
DID YOU KNOW?
Radio broadcasting in the early 20th century brought the first major consumer product, the broadcast receiver. Later products included telephones, televisions, and calculators, then audio and video recorders and players, game consoles, mobile phones, personal computers, and MP3 players.
Inductors and Their Applications
Inductors are passive components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them.
They are usually used in filtering applications, energy storage, and tuning circuits. Inductors come in various forms, including air-core, iron-core, and ferrite-core, each providing different levels of inductance and performance characteristics.
Air-core inductors are used in high-frequency applications where low inductance values are sufficient. Iron-core inductors provide higher inductance values, making them the best options for power applications.
Ferrite-core inductors offer a balance between performance and size and are commonly used in radio frequency circuits and power supplies.
The Importance of Chokes and Inductors
Chokes and inductors play a vital role in ensuring circuit efficiency and stability. They are used to filter out unwanted noise and interference, providing clean power to sensitive components.
In power supplies, chokes help maintain a stable voltage output, protecting devices from voltage spikes and fluctuations.
Inductors also play a major role in energy storage and transfer. In switch-mode power supplies, inductors store energy when the switch is on and release it when the switch is off, ensuring efficient energy conversion. This process reduces energy loss and improves overall circuit efficiency.
Combining Passive Components for Optimal Performance
The integration of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in a circuit is important for achieving optimal performance. Each component has a specific role, and their combined effects ensure the circuit operates as intended.
For example, in a low-pass filter circuit, a resistor and capacitor work together to allow low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency signals. Similarly, in an LC circuit, an inductor and capacitor create a resonant circuit used in tuning applications.
Practical Applications of Passive Components
Passive components find applications in various fields, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. In audio equipment, resistors and capacitors are used to shape sound quality, while inductors help filter out noise.
In telecommunications, these components are necessary for signal processing and transmission. In automotive electronics, passive components ensure the reliable operation of control systems and sensors.
Challenges and Considerations
While passive components are vital, their selection and implementation require careful consideration. Things like tolerance, temperature coefficient, and frequency response must be considered to ensure reliable performance.
On top of that, passive components can degrade over time, requiring regular inspection and replacement to maintain circuit integrity.
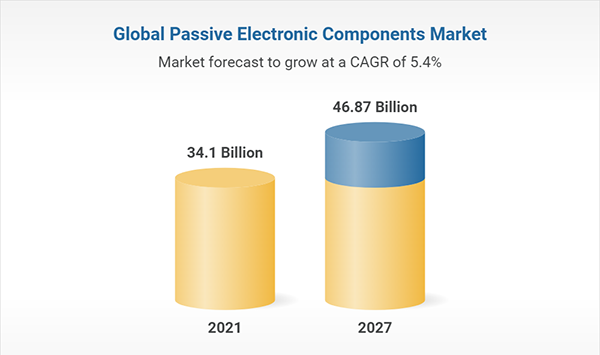
The global Passive Electronic Components market size was valued at USD 34820.33 Million in 2022 and will reach USD 53972.15 Million in 2028, with a CAGR of 7.58% during 2022-2028.
Future Trends in Passive Components
The demand for smaller, more efficient electronic devices drives innovation in passive component technology. Advances in materials and manufacturing techniques are leading to the development of components with higher performance and reliability.
For example, multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) are becoming pretty popular for their compact size and high capacitance values, meeting the needs of modern miniaturized electronics.
Conclusion
Passive components are indispensable in modern electronics, providing the foundation for reliable and efficient circuit operation. Understanding the roles and applications of resistors, capacitors, and inductors is vital for anyone involved in electronics design and maintenance.
As technology advances, the development of more efficient and compact passive components will continue to shape the future of electronics.