China is a digital powerhouse with an ever-expanding tech industry, presenting some great growth opportunities for global companies seeking global expansion.
However, unlocking the vast Chinese market requires more than just simply translating your software, It also demands a deep understanding of China’s unique cultural nuances, linguistic complexities, and regulatory landscape.
Another important factor often underestimated by developers is choosing the right software localization company. Businesses expanding their reach to the international market and planning to introduce their products in China should master this technique. It is essential to be aware of everything that can affect your performance and boost your brand image in the target market.
So, in this read, I will navigate you through the complete software localization. So from developing an understanding of the Chinese market to discussing the key components of software localization, here’s everything you need to know.
Understanding the Chinese User Base
So, to understand the Chinese user base you must consider the demographic and cultural variables, here take a look at them one by one:
1) Demographics and User Preferences
To effectively reach the Chinese market, it is essential to develop a proper understanding of the key user demographics and user behaviour and expectations. Under the light of these, China is divided into three sections:
- Age Groups: Young adults from age 18-34 (active online users, trend followers, social media activists, gamers, and online traders). Middle-aged adults from age 35-54 (preferences are work, education, and lifestyle management). Seniors aged 55 and above (a smaller segment, yet interested in using mobile apps for health and finance management and communication).
- Urban vs. Rural: Represents two different segments living in China. The first one—urban—has greater access to the latest technology and higher disposable income. Second is rural, a growing yet significant market.
2) Cultural Considerations
Chinese people are very sensible in terms of culture. They value their customs and rituals a lot. Understanding the local culture is crucial to leading the software industry in China. Cultural considerations include adjusting colours, images, symbols, and even the functionality of software according to the users.
Also, it is important to know the culturally preferred and restricted factors such as auspicious symbols, colours (red for good fortune), and numerology (avoiding the number 4 as it is associated with bad luck).
And,
Do You Know?
The Chinese software industry has been on a significant growth, where the market will reach $36.65 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow with an emphasis on AI, big data, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
Key Components of Software Localization
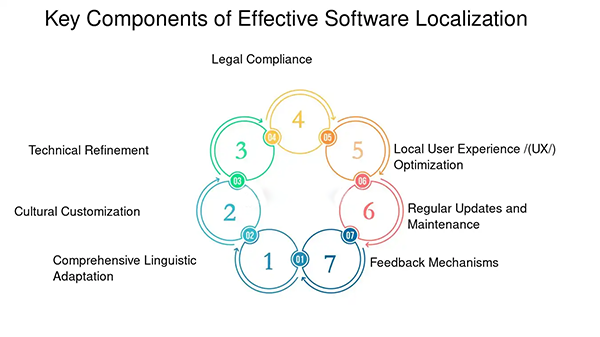
There are a range of components to be included in a software localization strategy, here take a look at some of them:
1) Language Translation
Translating the textual content in software is the basic yet essential step. There are various dialects of Chinese. Which one you choose while translating highly depends on the region you select. If you are targeting users in Mainland China, Singapore, or Malaysia, you will hit Simplified Chinese. If you are targeting Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macau, users there prefer traditional Chinese.
2) User Interface Adaptation
The UI of software must be fascinating. While localizing the user interface, be careful with the cultural nuances. Use specified words and idiomatic expressions with which the audience can easily relate. Chinese characters usually take up more space than English words. It can affect the whole design and UI of your software. Moreover, prefer localized terms to convey the intended meaning of your message naturally.
3) Functional Localization
By that, we mean integrating the localized payment systems commonly used in China for online shopping or in-app purchases. It also includes adapting date and time formats according to standards in different regions of China.
Technical Challenges in Localization
While there are a range of benefits of a localization strategy, there are also some technical challenges that come with it. So, let’s have a deep dive into them along with their ideal solutions.
1) Character Encoding and Fonts
The most common challenge in software localization is handling Chinese characters. They are complex and hard to handle. Furthermore, UTF-8 is specified character encoding for Chinese. It represents a wide range of characters that makes it essential for software localization. Other than that, Chinese dialects have different character sets that pose a challenge in adapting the software for a diverse audience.
2) Localization of Backend Systems
Adapting databases and services is crucial to support the Chinese content in software effectively. It begins with configuring databases for UTF-8 encoding that ensure proper retrieval of Chinese characters without corrupting the data.
3) Testing and Quality Assurance
Being a global company, ensuring the quality of the software is indeed a challenge. It requires a deep understanding of cultural nuances, knowledge of complex and technical terms, and most importantly, a native-like linguistic approach. Having such expertise might be difficult for a non-professional, but not for professional Chinese translation services. They understand the complexities involved in the localization of software and expertly handle the technicalities.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
There are basically two major compliance and regulatory requirements, let’s have a brief look at them:
1) Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Laws
Reaching the Chinese market with your software requires having a thorough understanding of local data privacy and cybersecurity laws. Every software company has to follow them in order to streamline their global reach and ensure success in the Chinese market.
2) Software Licensing and Approval
In China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) approves the companies to launch their software. However, some particular rules and regulations have to be followed by global software institutes at any cost.
Best Practices for Successful Localization
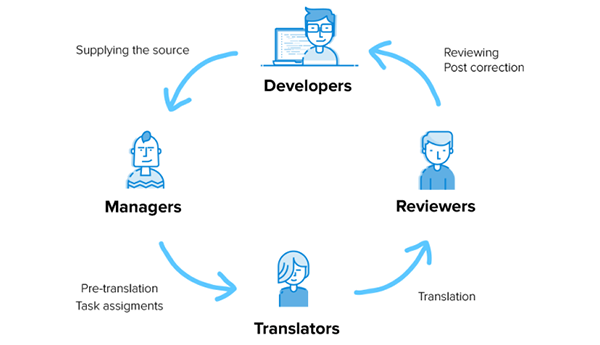
Here are some of the best practices for a successful localization:
1) Working with Native Linguists and Cultural Experts
Software localization is a complex process that can be done with high proficiency and expertise. Therefore, relying on non-professionals or free translation tools can harm your business and damage your brand image in the Chinese market. Always prefer to work with native linguists and cultural experts, as they provide the linguistically accurate and culturally appropriate translation of your software content.
2) Agile Localization and Continuous Updates
Localization is not a one-time process. It goes on with every update in your software, whether it is relevant to content, design, UI, or functionality.
The Chinese software industry is growing rapidly, generating massive expansion opportunities for global companies. However, reaching the Chinese market effectively requires mastering software localization and understanding the challenges and technicalities involved.